
And what strength these interactions do have requires that the interacting groups can approach each other closely (an angstrom or less).Most of hydrophilic and hydrophobic residues are thought to be exposed and buried in proteins, respectively. Noncovalent interactions are individually weak but collectively strong.Īll three forms of noncovalent interactions are individually weak (on the order of 5 kcal/mole) as compared with a covalent bond (with its 90–100 kcal/mole of bond energy). serine and threonine residues of proteins and.Between −C=O groups and hydroxyl (H-O−) groups in.between the −C=O group and the H-N− group of nearby peptide bonds in proteins giving rise to the alpha helix and beta configuration.a hydrogen atom which is covalently attached to a second strongly-electronegative atom.a strongly electronegative atom (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen) approaches.Increasing salt concentration reduces the strength of ionic binding by providing competing ions for the charged residues. The result: Again the net charge on the molecule changes (it becomes more negative) and, again, many of the opportunities its R groups have for electrostatic interactions with other molecules or ions are altered. H + are removed from the NH 3 + groups of Lys and Arg removing their positive charge.
H + are removed from the COOH groups of Asp and Glu, giving them a negative charge (COO −), and.The result: Not only does the net charge on the molecule change (it becomes more positive) but many of the opportunities that its R groups have for ionic (electrostatic) interactions with other molecules and ions are altered. H + bind to the unoccupied pair of electrons on the N atom of the amino (NH 2) groups of lysine (Lys) and arginine (Arg) giving them a positive charge.H + bind to the carboxyl groups (COO -) of aspartic acid (Asp) and glutamic acid (Glu), neutralizing their negative charge, and.Ionic interactions are highly sensitive to For example, as the figure shows, negatively-charged carboxyl groups on aspartic acid (Asp) and glutamic acid (Glu) residues may be attracted by the positively-charged free amino groups on lysine (Lys) and arginine (Arg) residues.
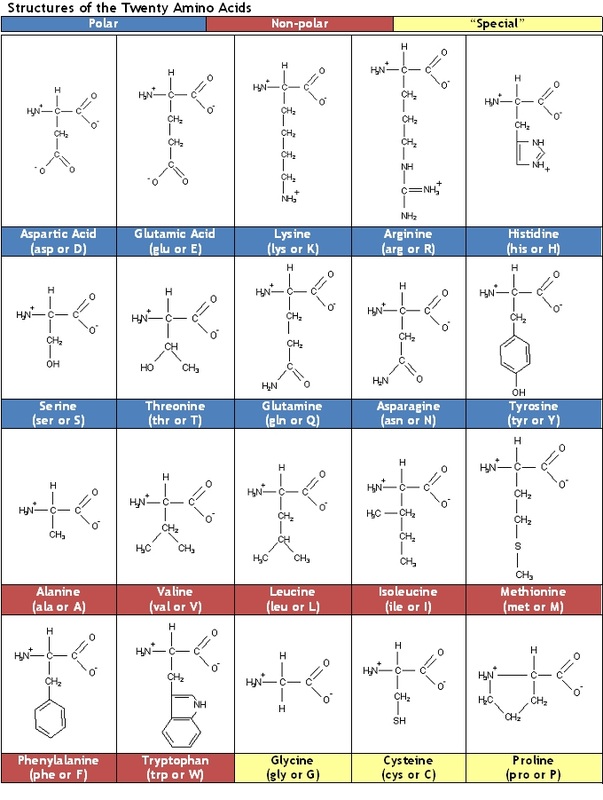
At any given pH, proteins have charged groups that may participate in binding them to each other or to other types of molecules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
